Imagine a world where every drop of liquid flows precisely where it's needed, thanks to a silent guardian—the gate valve. It's like a traffic controller which controls the flow of liquids, gases, and other substances in pipelines across a wide range of industries. It is essential for precision, durability, and managing high-pressure environments.

In this comprehensive guide, we will explore gate valves, its uses, mechanics, variations, and best practices. By the end, you will not only understand what gate valves are but also know their important role in various industries.
What are Gate Valves?
Imagine a gatekeeper at a castle, controlling who enters and who stays out. Gate valves do the same but for fluids in pipelines. It features a simple and effective flat gate that slides across the path of the fluid, controlled by a handwheel. This mechanism allows for complete flow control—either fully open or fully closed under both low and high-pressure scenarios. Gate valves are ideal for applications requiring precise flow control.
Market Growth of Gate Valves
The global gate valve manufacturing market is expected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of over 4.1% from 2022 to 2029. Here are the key insights:
- The global gate valve supplier market is expected to reach $12.99 billion by 2028, driven by growth in oil & gas, power generation, and water treatment sectors due to their versatility and reliability.
- From 2023 to 2033, revenues are expected to exceed US$ 24.3 billion at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.0%.
- Gate valves, specifically wedge gate valves, experienced robust sales growth with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 4.8% from 2018 to 2022.
What are the Types of Gate Valves?
Gate valves come in various types, each tailored to specific applications and environments. Let's look at the main ones:
Wedge Gate Valves
Wedge gate valves are one of the most common gate valves which is mostly found in plumbing and industrial pipeline setups. They come in various subtypes like solid wedge, flexible wedge, and split wedge.
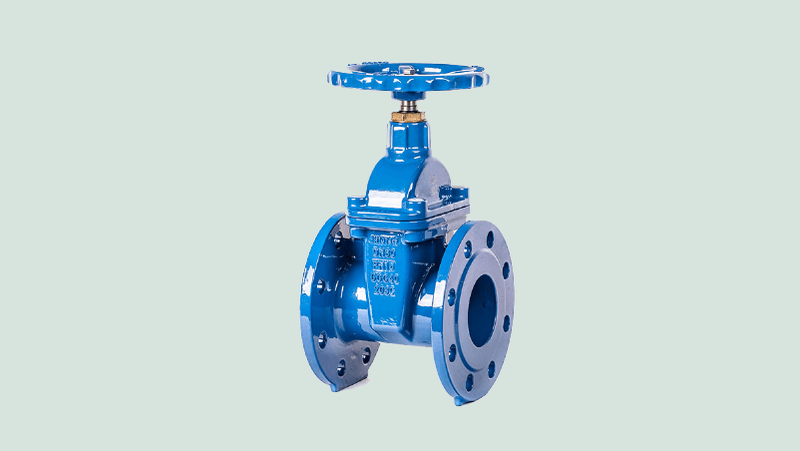
- Solid wedge valves : aka plain wedge are strong and simple, and are versatile for different fluid media and turbulent flows because of their robust single-piece design.
- The split wedge gate valve : has a two-piece design with a bevelled face that seals against the seat in the closed position. This design makes it easier to open and close than the solid wedge, but it is not as durable and can wear over time.
- Flexible wedge gate valve : is a single-piece design with a flexible seal that conforms to the seat in the closed position. This design offers effortless operation, but it is not as durable as the other two types and can leak if not properly maintained.
These wedge gate valves are commonly used in oil, gas, water, sea water and steam lines as on/off and isolation valves.
Parallel Gate Valves
Parallel gate valves operate similarly to wedge gate valves, but with two disks at a 90-degree angle to the flow direction. They are mostly utilised in high-temperature settings as they reduce the risk of thermal binding.
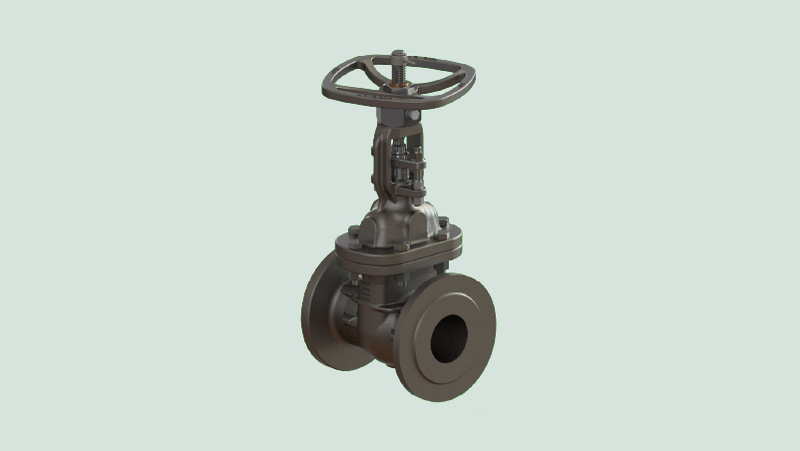

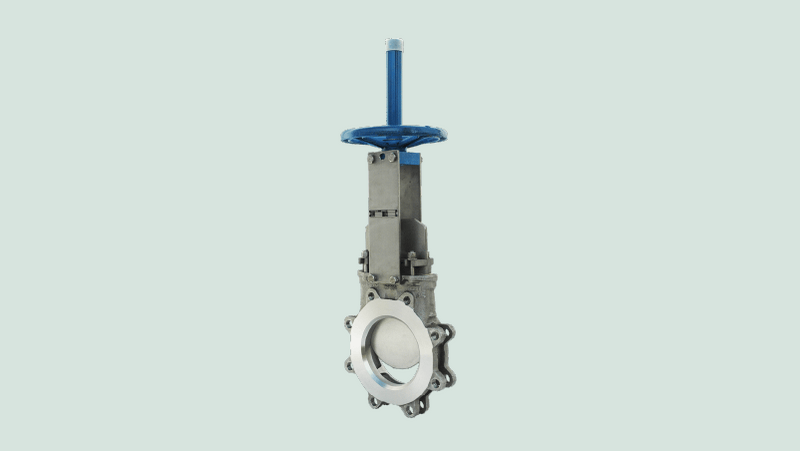
Knife Gate Valves
These valves are specifically designed for thick or viscous fluids like slurry. They have tapered disks that facilitate cutting through dense material, ensuring smooth closure even in challenging conditions.
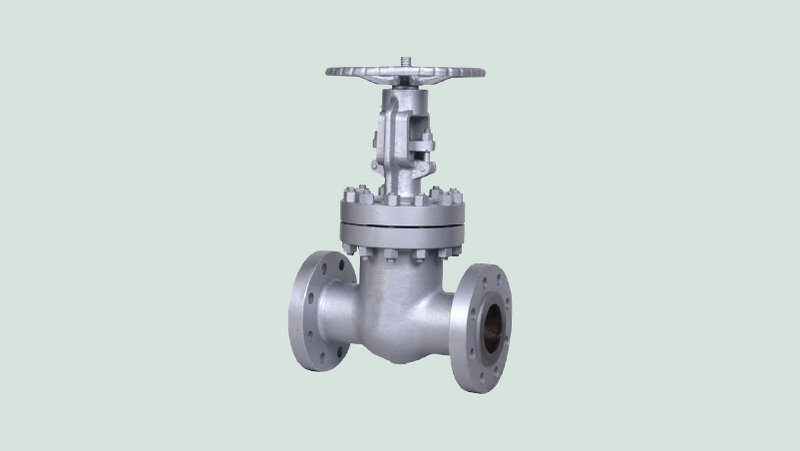
Flanged Gate Valves
It features a body flanged and bolted to the bonnet. It is ideal for high-pressure applications. Although they are not as specialised as pressure sealing models, they still offer robust performance in tough conditions and deliver strong performance.
Get Different types of gate valves based on your needs. Explore our wide range of Gate valves.
What are the Components of Gate Valve?
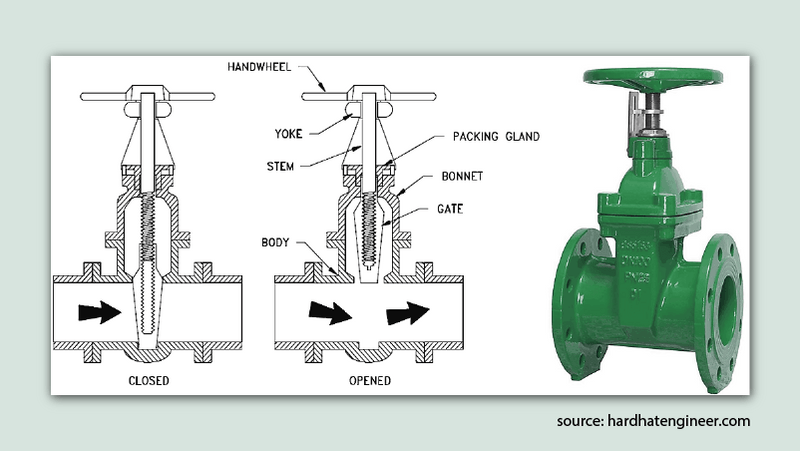
A gate valve comprises of several key parts:
- Handwheel : It is a manual operation component which is used to open or close the valve. It helps move the gate inside.
- Stem : The stem is connected to the handwheel and extends into the valve body. It transmits the motion from the handwheel to the gate, raising or lowering it when required.
- Gasket : The gasket ensures a tight and leak-proof seal between the bonnet and the valve body. It prevents any fluid from escaping through the connection points.
- Bonnet : The bonnet houses the stem and other internal valve components. It also provides protection to these components and maintains the integrity of the seal.
- Valve Body : The valve body contains the gate and acts as the main structure of the valve. It provides the necessary support and alignment for the gate and other internal parts.
- Flange : The flange is the connection point of the valve to the pipeline or application. It allows for easy installation and removal of the valve when necessary.
- Gate : The gate is the movable component that controls the flow of fluid. It moves up or down within the valve body to either allow or block the passage of fluid.
How Does the Gate Valve Work?
Gate valves are widely used in various industries to control the flow of liquids and gases. The working mechanism of gate valves is simple yet highly effective. Their operation relies on the straightforward movement of the gate which makes them reliable for various applications.
Below we have shared a step-by-step guide on how a gate valve works:
Installation
The gate valve is installed within a pipeline, either above ground or below, to regulate the flow of fluids like water, oil, or gas.
Gate or Disk Barrier
Within the valve, there is a gate or disk that functions as a barrier. This gate can be raised to allow fluid flow or lowered to block it completely.
Handwheel Control
Handwheel located on the valve bonnet is used to control the gate.
Opening the Valve
Turning the handwheel clockwise lifts the gate, creating an open pathway for fluid to pass through. When the gate is fully opened, the gate valve offers minimal resistance to the flow, resulting in a very small pressure drop.
Closing the Valve
Conversely, turning the handwheel in the opposite direction, typically anticlockwise, lowers the gate back into position, sealing off the pathway and stopping fluid flow.
Bidirectional Flow Control
The bidirectional design of gate valves can block fluid movement in both upstream and downstream directions when the gate is in the closed position.
Gate valves can be operated in three different way:
- Manual Gate Valve : Operated by turning the handwheel. They are cost-effective and suitable when you don't need to open and close them often.
- Pneumatic Gate Valve : These use compressed air for operation. They're great for remote control without the need for manual intervention.
- Electric Gate Valve : Electric gate valves run on electric motor. They are handy for remote control and can be integrated into automated systems for enhanced functionality.
Each actuation method has its advantages and is chosen based on the specific requirements of the application, including the frequency of operation, accessibility, and automation needs.
What are the Applications of Gate Valves?
Gate valves are not just ordinary components, they are the backbone of efficiency in various sectors. Their robust construction and ability to withstand high pressures make them particularly valuable in environments where reliable fluid control is paramount. They are used in various industries including:
- Water Treatment
- Energy Sector
- Manufacturing
- Chemical Processing
- Power Generation
- HVAC Systems
- Marine Industry
- Water Gate Valves
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Gate Valves?
The advantages of gate valves are multifaceted, encompassing:
- Simple design
- Easy to operate and maintain
- Excellent Shut-Off Capability
- Minimal pressure drop and energy loss .
- Bi-directional flow
- Durable and suitable for extreme temperature and pressure
- Tight Sealing
- Available in various sizes
Disadvantages of Gate Valves:
- Slow Opening and Closing Time: Drawback in situations requiring quick flow control.
- Clogging: They are susceptible to clogging where high cleanliness or hygiene standards are required.
- Corrosion Susceptibility: Leaks and reduced durability if not properly maintained.
- Bulkier size compared to other valves.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Gate Valves
Proper maintenance is crucial for ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of gate valves. This includes:
- Regular inspections
- Lubrication
- Operational Testing
- Cleaning
- Replacing worn parts
- Addressing leakage
By regularly maintaining gate valves you can keep gate valves in prime condition as well as ensure optimal performance and minimise downtime, preventing costly repairs. Furthermore, there are various benefits of buying directly from B2B manufacturers like expert guidance, maintaining tips, assistance in choosing right products and more.
The Future of Gate Valves
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, gate valves are undergoing notable advancements:
Robotic Precision
Automated testing processes, ensure that each gate valve meets stringent safety and performance standards before being deployed in various applications. This robotic precision guarantees consistent and reliable valve functionality.
Environmental Focus
Gate valve manufacturers use energy-efficient designs, advanced sealing mechanisms, and predictive maintenance systems. By integrating these eco-friendly features, gate valves contribute to sustainable practices in fluid control systems across industries.
These innovations represent a forward-thinking approach in the evolution of gate valves.
Conclusion
Gate valves are not just components, they are enablers of efficiency, reliability, and safety across industries. Understanding their intricacies and embracing innovations ensures a seamless flow of operations and a sustainable future.
Want to enhance your industrial process and fluid control? Get precision engineered gate valves from top manufacturers?